The Miracle of el blastocisto gif in the Uterine Wall
The human reproductive process is filled with extraordinary complexity. Among the critical stages is the implantation of the blastocyst into the uterine wall. This pivotal step plays a fundamental role in establishing pregnancy, with deep implications for fertility, pregnancy health, and reproductive challenges. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the fascinating process of how the blastocyst implants itself in the uterine wall, outlining each stage and its significance.
What is the Blastocyst?
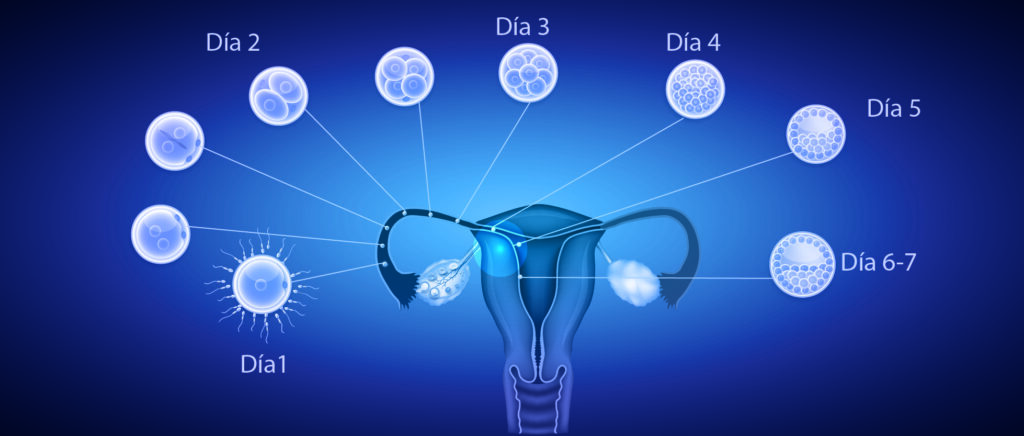
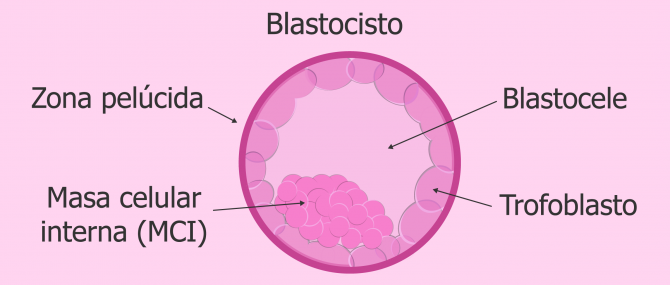
Before delving into the process of implantation, it’s essential to understand the blastocyst. The blastocyst is a stage of early embryo development, typically occurring five to six days after fertilization. At this point, the embryo has developed into a cluster of 70-100 cells, divided into two main components: the inner cell mass, which will develop into the fetus, and the trophoblast, which will form the placenta.
Key Takeaways:
- The blastocyst forms around five to six days after fertilization.
- It contains the inner cell mass (future fetus) and trophoblast (future placenta).
- The blastocyst is very small, measuring around 0.1 to 0.2 millimeters in diameter, only visible under a microscope.
The Significance of Blastocyst Implantation
Implantation is a critical step in pregnancy. It marks the moment when the blastocyst connects with the mother’s body, establishing a life-sustaining bond. Without successful implantation, pregnancy cannot progress, even if fertilization has occurred.
Key Takeaways:
- Implantation is essential for pregnancy continuation.
- It begins communication between the embryo and the mother’s body.
- The implantation process triggers the release of pregnancy hormones, such as hCG, vital for sustaining the pregnancy.
The Uterine Wall: Preparing for Implantation
The uterine wall, specifically the endometrium, must be in optimal condition to support implantation. Factors such as thickness, blood flow, and hormonal balance play key roles in ensuring that the uterus is a receptive environment for the blastocyst.
Key Takeaways:
- The endometrium thickens during the menstrual cycle to prepare for possible implantation.
- Hormones like estrogen and progesterone regulate the receptivity of the uterine lining.
- A well-prepared uterine environment is crucial for the blastocyst to implant successfully.
A Step-by-Step Guide to the Implantation Process
The implantation process unfolds in a series of highly coordinated steps. Each stage is crucial in ensuring that the blastocyst successfully attaches to the uterine wall.
Arrival at the Uterus
After fertilization in the fallopian tube, the blastocyst travels toward the uterus. This journey typically takes five to seven days. By the time it reaches the uterus, the blastocyst is ready to implant.
Apposition
In this initial stage, the blastocyst loosely attaches to the uterine wall. It searches for the best location to begin the implantation process.
Adhesion
Once a suitable spot is found, the blastocyst firmly attaches to the uterine lining. The trophoblast cells are responsible for this firm adhesion, interacting closely with the endometrial cells.
Invasion
In the final step, the trophoblast cells invade the uterine lining, embedding the blastocyst deeply within the endometrium, securing it for continued development.
Key Takeaways:
- The journey from fertilization to implantation takes about a week.
- The process involves apposition, adhesion, and invasion.
- Trophoblast cells play a critical role in securing the blastocyst within the uterine wall.
The Role of Hormones in Implantation
Hormonal regulation is vital to the implantation process. Estrogen and progesterone are the primary hormones responsible for preparing the endometrium and supporting the early stages of pregnancy.
Key Takeaways:
- Estrogen thickens the uterine lining and increases blood flow, creating a nurturing environment for the blastocyst.
- Progesterone stabilizes the endometrial lining and encourages the secretion of nutrients to support the blastocyst’s development.
- A delicate balance between these hormones is crucial for successful implantation.
Factors Affecting Implantation Success
Several physiological and environmental factors can influence the success of the implantation process. Understanding these factors is important for optimizing reproductive health and increasing the likelihood of a successful pregnancy.
Uterine Health
Conditions such as endometriosis, fibroids, or a thin endometrial lining can impede implantation.
Hormonal Imbalances
Fluctuations in estrogen or progesterone can create unfavorable conditions for implantation.
Lifestyle Factors
Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor diet can negatively affect the uterine environment.
Age
Advanced maternal age is associated with reduced egg quality and alterations in the uterine environment, impacting implantation success.
Key Takeaways:
- A healthy uterine environment is essential for successful implantation.
- Hormonal balance ensures the endometrium remains receptive.
- Lifestyle choices and age can significantly affect implantation outcomes.
Challenges Related to Implantation Failure
Unfortunately, implantation failure is not uncommon and can lead to early pregnancy loss or other complications. Understanding the reasons for implantation failure is key to addressing fertility challenges.
Early Pregnancy Loss
Many early miscarriages are a result of failed implantation, often due to chromosomal abnormalities in the embryo or issues with the uterine lining.
Infertility
Recurrent implantation failure may contribute to infertility, requiring medical intervention such as hormonal therapy or assisted reproductive techniques.
Ectopic Pregnancy
In rare cases, the blastocyst may implant outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube. This dangerous condition, known as ectopic pregnancy, requires immediate medical intervention.
Key Takeaways:
- Implantation failure is a common cause of early pregnancy loss.
- Recurrent implantation failure can lead to infertility.
- Ectopic pregnancy is a serious complication of improper implantation.
The Role of Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
Advancements in medical science have provided new avenues for couples facing implantation difficulties. Assisted reproductive technologies (ART), such as IVF and embryo transfer, offer hope for overcoming these challenges.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
IVF involves fertilizing an egg outside the body and then transferring the resulting blastocyst into the uterus. This allows for better control over implantation timing.
Embryo Transfer
Careful timing of embryo transfer increases the likelihood of successful implantation by ensuring the uterine environment is optimal.
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
PGT allows for the screening of embryos for genetic abnormalities, improving the chances of a healthy pregnancy.
Key Takeaways:
- ART has revolutionized treatment for implantation-related fertility issues.
- IVF and embryo transfer offer more control over implantation timing.
- PGT improves the chances of successful implantation by screening for healthy embryos.
Nutrition and Lifestyle: Supporting Implantation Success
Healthy lifestyle choices and proper nutrition are essential for creating an optimal environment for implantation. By nourishing the body, you improve the chances of successful implantation.
Nutrition
A diet rich in whole foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats supports uterine health.
Folic Acid
Folic acid is crucial for early pregnancy development, aiding in cell division and DNA synthesis.
Exercise
Moderate physical activity enhances blood flow to the uterus but should not be excessive, as over-exercising can disrupt hormonal balance.
Stress Management
Reducing stress through techniques like meditation and yoga can improve overall reproductive health.
Key Takeaways:
- Proper nutrition supports a healthy uterine environment.
- Folic acid is vital for early pregnancy.
- Moderate exercise and stress management positively impact reproductive health.
Conclusion: Appreciating the Wonder of Implantation
The implantation of the blastocyst into the uterine wall is a remarkable event that initiates the process of life. It is a delicate, intricate process that requires perfect hormonal regulation, a receptive uterine lining, and a healthy blastocyst. By understanding implantation, we deepen our appreciation for the complexities of reproduction and gain insight into the importance of maintaining reproductive health.