The ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram transmission, particularly in its later iterations, is a renowned automatic gearbox utilized in various high-performance vehicles. Its seamless shifting and efficient operation rely heavily on a network of solenoids located within the valve body. These solenoids function as electronically controlled valves, regulating fluid pressure to engage specific clutches and achieve desired gear changes. If you’re a technician working on a ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram transmission, grasping the solenoid diagram is crucial for accurate diagnosis and repair.
Understanding the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram, equipping you with the knowledge to:
- Identify the various solenoids and their roles.
- Interpret the hydraulic pressure flow within the valve body.
- Troubleshoot potential issues related to solenoid failure.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a solid foundation for navigating the complexities of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram transmission.
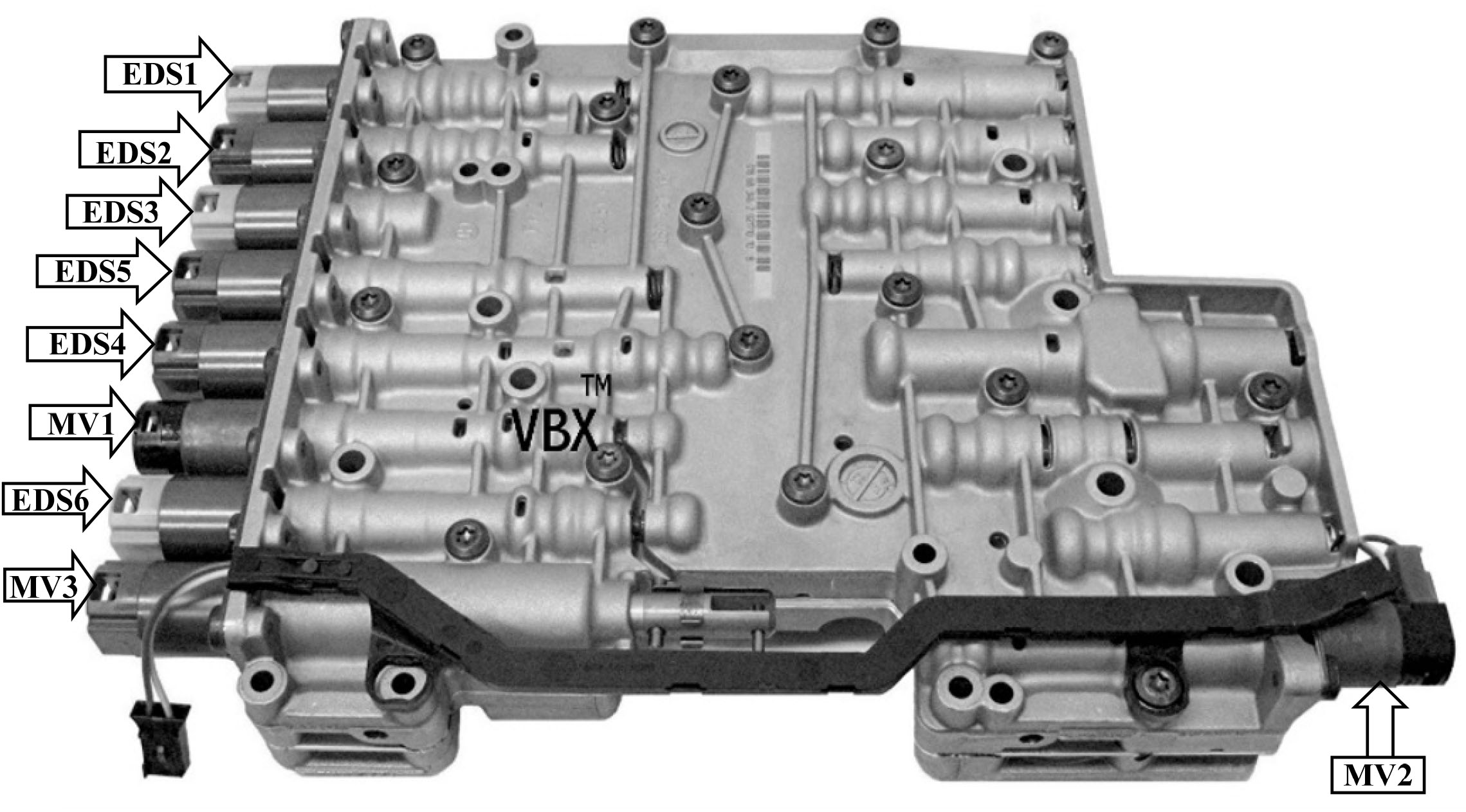
Identifying the Components of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram
The first step involves familiarizing yourself with the individual solenoids present in the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram. Here’s an overview of the common solenoids you will encounter:
- Pressure Control Solenoids (EDS): These solenoids regulate the overall line pressure within the transmission. Typically, there are several EDS solenoids, each designated by a number (EDS 1, EDS 2, etc.) that manages a specific pressure area.
- Shift Solenoids (SL): These solenoids control the application of specific clutches by directing hydraulic pressure. Common examples include the SL1 solenoid for the A/C clutch and the SL2 solenoid for the B clutch.
- Torque Converter Lockup (TCC) Solenoid: This solenoid manages the engagement of the torque converter clutch, enhancing fuel efficiency during cruising speeds.
- Manual Valve (MV): Sometimes referred to as the EPC (Electronic Pressure Control) solenoid, this component regulates the overall pressure directed to the shift solenoids, influencing shift characteristics.
It’s important to note that the exact arrangement and nomenclature of solenoids may vary slightly based on the vehicle application. Always consult your specific ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram service manual for the most accurate information.
Interpreting the Solenoid Diagram
A solenoid diagram serves as a schematic representation of the valve body, illustrating the location and functionality of each solenoid. Here’s how to interpret the key elements of a ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram:
- Solenoid Symbols: Each solenoid is represented by a unique symbol, often a rectangle with internal markings indicating its function (pressure control, shift, etc.).
- Fluid Pathways: Lines within the diagram depict the flow routes of hydraulic fluid throughout the valve body. These lines connect solenoids, control valves, and clutch cylinders.
- Directional Arrows: Arrows on the lines indicate the direction of fluid flow when a particular solenoid is activated.
- Pressure Levels: Some diagrams may incorporate color coding or labels to represent different pressure levels within the system.
Understanding these components allows you to trace the path of hydraulic pressure as it is modulated by the solenoids. For example, during a specific gear change scenario, by following the activation of a particular shift solenoid and the corresponding fluid path through the valve body, you can visualize how the clutch engages and the gear change occurs.
Common Solenoid-Related Problems in ZF 6HP Generation 2 Transmissions
Solenoids are electronic components that may wear out over time. Here are some common issues associated with malfunctioning solenoids:
- Shifting Problems: Erratic gear changes, delayed engagement, or slipping between gears can indicate a faulty shift solenoid.
- Line Pressure Issues: A failing pressure control solenoid can lead to inadequate or excessive line pressure, resulting in harsh shifts or lack of power transfer.
- Torque Converter Shudder: A malfunctioning TCC solenoid may cause vibrations during torque converter lockup.
Replacing and Repairing ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoids
While basic troubleshooting steps can be performed, replacing or repairing solenoids within the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram valve body is best left to experienced technicians. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Valve Body Disassembly: The transmission must be removed from the vehicle, and the valve body carefully disassembled following the service manual. This involves removing various valves, springs, and seals.
- Solenoid Replacement: Faulty solenoids are identified and replaced with new OEM or high-quality aftermarket parts. Ensure proper cleaning and lubrication of surrounding components during this process.
- Valve Body Reassembly: The valve body is reassembled meticulously, ensuring all components are placed correctly and torqued to specification. Special attention should be given to valve clearances and proper alignment.
- Transmission Reinstallation and Calibration: Once the valve body is reinstalled within the transmission, the entire unit is mounted back onto the vehicle. In some cases, the transmission control module (TCM) may require reprogramming or calibration to adapt to the new solenoids.
Importance of Using Quality Components and Following Procedures
Utilizing high-quality replacement solenoids is crucial. Inferior parts can lead to premature failure and further transmission issues. Additionally, adhering to the service manual’s disassembly and reassembly procedures is vital to ensure proper functionality and prevent leaks or malfunctions.
Additional Resources for ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Information
For a deeper understanding of the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram and valve body operation, consider these resources:
- ZF Technical Documentation: ZF provides technical documentation and repair manuals for their transmissions. While some information may require a paid subscription, it can be an invaluable resource for professional technicians.
- Transmission Parts Suppliers: Reputable transmission parts suppliers often provide detailed catalogs with information on specific solenoids compatible with the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram. These catalogs may include technical specifications and solenoid replacement procedures.
- Online Repair Forums: Online forums frequented by experienced transmission builders and technicians can offer valuable insights and troubleshooting tips related to ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmissions.
Conclusion
By comprehending the ZF 6HP Generation 2 solenoid diagram, you gain an essential perspective on the internal workings of this sophisticated transmission. This knowledge empowers you to diagnose potential solenoid-related issues and perform fundamental troubleshooting steps. Remember, for complex repairs involving disassembly and reassembly of the valve body, it is highly recommended to consult a qualified transmission specialist.
FAQ’s
Here are 10 FAQs related to the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram:
1. What is the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission?
The ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission is an automatic gearbox used in various high-performance vehicles, known for its smooth shifting and efficiency.
2. What role do solenoids play in the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission?
Solenoids in the transmission act as electronically controlled valves that regulate hydraulic fluid pressure to engage clutches and facilitate gear changes.
3. How many solenoids are typically found in the ZF 6HP Generation 2?
The transmission usually contains multiple solenoids, including pressure control solenoids (EDS), shift solenoids (SL), torque converter lockup solenoids (TCC), and manual valves (MV).
4. What are the symptoms of a failing shift solenoid?
Common symptoms include erratic gear changes, delayed engagement, and slipping between gears, which may indicate a faulty shift solenoid.
5. How can I diagnose solenoid-related issues in my transmission?
You can diagnose solenoid-related problems by checking for transmission error codes, observing shifting behavior, and conducting pressure tests.
6. Is it safe to replace solenoids myself?
While basic troubleshooting can be done by a knowledgeable technician, replacing solenoids involves disassembling the transmission and is best left to experienced mechanics.
7. What tools do I need to replace solenoids in the ZF 6HP Generation 2 transmission?
Tools typically needed include a socket set, torque wrench, screwdrivers, and a service manual for reference during disassembly and reassembly.
8. How often should solenoids be replaced?
Solenoids do not have a specific replacement interval, but they should be inspected regularly, especially if you notice shifting issues or fluid leaks.
9. Can using low-quality solenoids affect my transmission?
Yes, using low-quality or incompatible solenoids can lead to premature failure and additional transmission problems, affecting performance and reliability.
10. Where can I find more information on the ZF 6HP Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram?
Additional information can be found in ZF’s technical documentation, reputable transmission parts suppliers, and online forums focused on transmission repair and maintenance.

